Preventive maintenance refers to routine procedures that help minimize equipment failure and reduce unplanned downtime. By implementing these practices, businesses can ensure smooth operations and avoid costly disruptions. These routines typically include inspections, lubrication, and adjustments. Beyond manual tasks, preventive maintenance also involves careful planning, scheduling, and documentation of past service reports and inspections. Industries that rely heavily on machinery—such as oil and gas, manufacturing, and mining—often use preventive maintenance to keep their operations running efficiently and safely. Preventive maintenance is any regular maintenance performed at scheduled intervals to reduce the risk of equipment failure. It includes activities such as inspections, cleanings, part replacements, and repairs. The main goal of preventive maintenance is to ensure that equipment functions as intended by the manufacturer. It also helps prevent accidents, reduces unexpected downtime, and lowers repair costs over time. Implementing a preventive maintenance program offers several benefits, including improved efficiency, cost savings, and enhanced safety. It helps companies avoid expensive emergency repairs and maintain compliance with industry regulations. Compared to reactive maintenance—which only addresses issues after they occur—preventive maintenance is generally more cost-effective. Reactive approaches often lead to higher expenses and extended downtime. Regular equipment checks allow businesses to be proactive rather than reactive, preventing failures before they happen. This approach can also support long-term budgeting and strategic planning for future goals. By focusing on prevention, companies can avoid many common operational issues. Here are some key benefits of a well-executed preventive maintenance strategy: Unplanned downtime can be extremely costly. According to research, production interruptions due to equipment failure can cost up to $260,000 per hour. Preventive maintenance helps reduce this risk by keeping machinery in optimal condition. It also helps maintain customer trust and ensures smoother business operations. When maintenance is planned, it’s less disruptive and easier to manage. Regular maintenance extends the life of machinery. Routine inspections and servicing ensure that assets remain functional for longer periods, reducing the need for frequent replacements. This not only saves money but also allows companies to allocate resources to other critical areas of the business. An inspector recording the operation of oil and gas process Maintained equipment is safer to operate. Preventive maintenance reduces the likelihood of malfunctions, which in turn lowers the risk of workplace accidents. When workers know that machines are regularly checked and serviced, they feel more secure. This leads to better morale and lower insurance and compensation costs for the company. Many industries have strict guidelines regarding equipment maintenance. Failing to meet these standards can result in fines or legal action. A consistent preventive maintenance schedule ensures that all equipment operates within required parameters, helping companies stay compliant and avoid penalties. While preventive maintenance is highly effective, it's not without its challenges. Companies should consider the following limitations when designing their maintenance plans: Even with the best preventive strategies, some failures are unavoidable. Natural disasters, human error, or unforeseen circumstances can still cause equipment breakdowns. Some assets lack advanced monitoring systems, making it difficult to predict potential failures. In such cases, traditional methods may not be sufficient, and predictive maintenance might offer better results. Although less expensive than reactive maintenance, preventive measures do require an initial investment. Small businesses with tight budgets may find it challenging to implement comprehensive programs. Performing preventive maintenance can take time, especially if it requires shutting down equipment. For businesses operating at full capacity, finding the right window for maintenance can be difficult. Effective preventive maintenance often requires additional staff or extended hours for existing employees. Proper training and resource allocation are essential to success. Excessive maintenance can waste time, money, and effort. It’s important to tailor the plan to the actual needs of the equipment, using data to guide decisions. There are three main types of preventive maintenance: Time-based maintenance is performed at regular intervals, regardless of how much the equipment is used. This is ideal for tasks like changing air filters every three months. However, it can sometimes lead to unnecessary work, especially if the equipment isn’t used frequently. Usage-based maintenance focuses on how often equipment is used. For example, cars require maintenance after a certain number of miles driven. This approach avoids over-maintenance and ensures that resources are used where they're most needed. Condition-based maintenance uses real-time data to determine when maintenance is needed. It relies on signs of wear, such as unusual sounds, temperature changes, or vibrations. This method is highly effective and can be just as reliable as other forms of preventive maintenance. Each type of preventive maintenance includes specific tasks, which can be categorized based on priority and urgency. These tasks may be time-based, usage-based, condition-based, or a mix of all three. Common task categories include mandatory, non-mandatory, pyramiding, inspection, and task-oriented tasks. Each plays a role in maintaining efficient and safe operations. A preventive maintenance checklist is a list of tasks that should be completed as part of a broader maintenance plan. It helps ensure that nothing is overlooked and that all necessary steps are followed. Checklists are usually developed with input from maintenance managers, workers, and regulatory bodies. Many companies use software to track and document their checklists effectively. A good checklist improves efficiency, reduces errors, and enhances safety. It also supports better planning and consistency across teams. Additional benefits include faster inspections, better diagnostics, and more specialized training for workers. Checklists vary by industry, but they all aim to ensure that equipment is properly maintained. Below are examples for different sectors: Drones are becoming a powerful tool in preventive maintenance. They allow for quick and safe visual inspections of hard-to-reach areas without disrupting operations. Using drones like the Elios 3, companies can monitor equipment conditions in real-time, reducing the need for scaffolding and minimizing downtime. They also keep workers out of dangerous environments. In one case study, the Elios 3 was used to inspect water infrastructure, creating detailed LiDAR maps to track asset wear and tear over time. Drones not only save time and money but also enhance worker safety, making them a valuable addition to any preventive maintenance strategy. Big size (up to 12"), ultra-abrasion, high/low temperature and corrosion resistant, and multiple length choices, Letone industrial hose are ideal for industries like construction, chemical, bulk material delivery, steel mills, oil & gas, machinery and equipment manufacturing, high pressure cleaning, F&B and applications of extremely working environment. Industrial Hose,Pumping Hose,Oilfield Hose,Concrete Hose Luohe Letone Hydraulic Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.litonghose.comPreventive Maintenance: A Comprehensive Guide
What Is Preventive Maintenance?
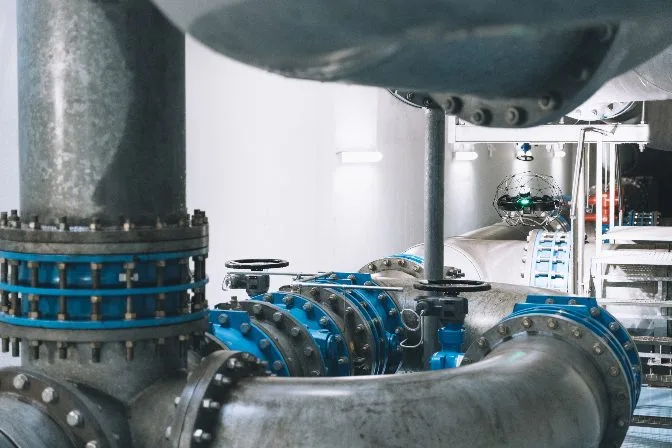 The Elios 3 inspecting a water management system
The Elios 3 inspecting a water management systemWhy Is Preventive Maintenance Important?
Advantages of Preventive Maintenance
Minimizes Downtime
Maximizes Equipment Lifespan
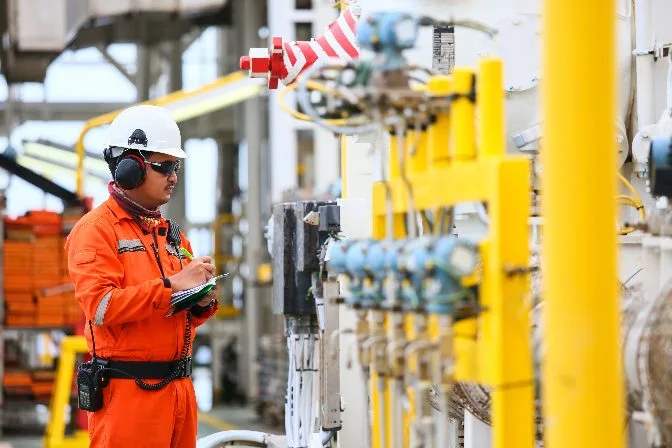

Helps Keep Workers Safe
Helps Ensure Regulatory Compliance
Limitations of Preventive Maintenance
Success Rate
Technological Constraints
Up Front Costs
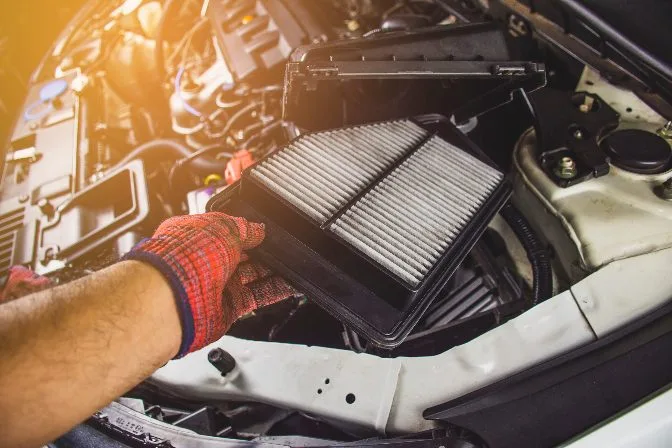 Changing a car filter
Changing a car filterTime Constraints
Worker Limitations
Over Maintenance
What Are the Types of Preventive Maintenance?
Time-Based Maintenance
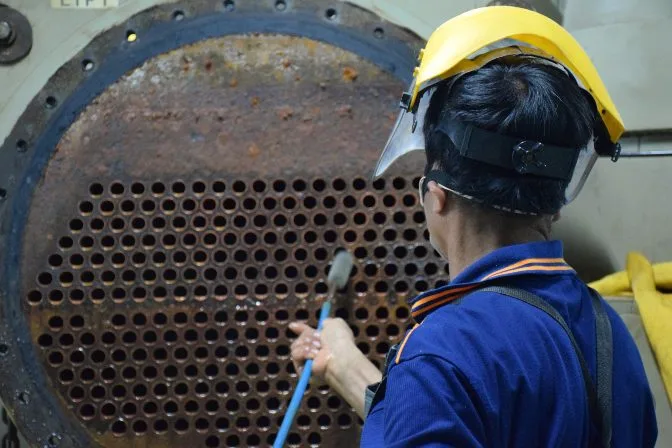 Cleaning a condenser tube from a chiller
Cleaning a condenser tube from a chillerUsage-Based Maintenance
Condition-Based Maintenance
Types of Preventive Maintenance Tasks
What is a Preventive Maintenance Checklist?

Benefits of a Preventive Maintenance Checklist
Preventive Maintenance Checklist Examples
Building Interior Preventive Maintenance Checklist
Network and Data Systems Preventive Maintenance Checklist
Semi Truck Preventive Maintenance Checklist
Drones in Preventive Maintenance
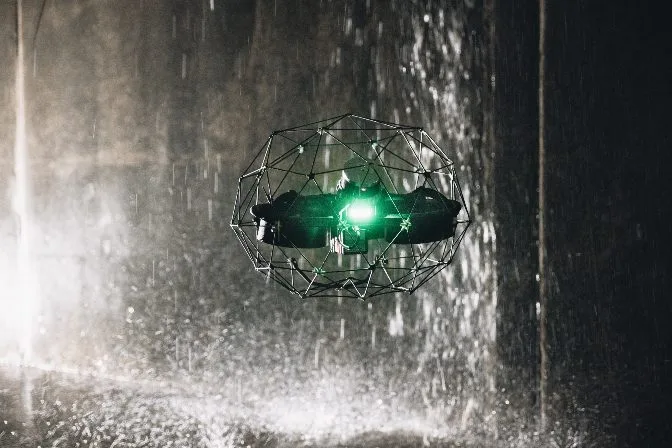 An Elios 3 drone performing a visual inspection
An Elios 3 drone performing a visual inspection