Preventive maintenance refers to the regular tasks and procedures performed to minimize equipment failure and unplanned downtime. These activities help ensure that machinery and systems operate efficiently and safely over time. It includes a variety of actions such as inspections, lubrication, and adjustments. Beyond physical upkeep, it also involves planning, scheduling, and documenting all maintenance activities. This approach helps organizations stay organized and proactive in managing their assets. Industries like manufacturing, oil and gas, and mining rely heavily on preventive maintenance to keep operations running smoothly. By maintaining equipment regularly, companies can avoid costly breakdowns and extend the life of their machinery. Preventive maintenance is any routine activity carried out at scheduled intervals to reduce the risk of equipment failure. It may involve cleaning, part replacements, or minor repairs before issues arise. The main goal is to maintain equipment performance and prevent unexpected breakdowns. It also supports workplace safety, reduces repair costs, and ensures compliance with industry standards. Implementing a preventive maintenance strategy offers numerous benefits, including reduced downtime, improved safety, and cost savings. It allows companies to address potential problems before they escalate into major failures. Compared to reactive maintenance—where repairs are done only after a breakdown—preventive maintenance is more cost-effective and less disruptive. Reactive approaches often lead to higher expenses and extended production halts. Regular checks and maintenance not only protect equipment but also create a safer working environment. Employees are less likely to be exposed to hazards when machines are well-maintained and functioning properly. Additionally, preventive maintenance helps businesses meet regulatory requirements and avoid fines. It’s an essential component of a long-term operational strategy. By addressing issues before they become critical, preventive maintenance helps maintain smooth operations and improves overall efficiency. Here are some key benefits: Unplanned equipment failures can be extremely costly, sometimes leading to losses of hundreds of thousands of dollars per hour. Preventive measures help ensure that maintenance is scheduled and predictable, reducing disruptions. This reliability strengthens customer relationships and avoids revenue loss due to delays. Regular servicing extends the life of machinery by preventing wear and tear. Well-maintained equipment performs better and requires fewer replacements, saving money in the long run. This also allows companies to allocate budgets toward innovation and growth rather than constant equipment purchases. An inspector recording the operation of oil and gas process Maintained equipment is less likely to malfunction, reducing the risk of accidents. This directly contributes to a safer workplace and lowers insurance and compensation costs. Preventive maintenance also minimizes the need for emergency repairs, which can expose workers to dangerous conditions. Many industries have strict regulations regarding equipment maintenance. Failing to comply can result in penalties or legal issues. Regular maintenance schedules help ensure that all requirements are met. While highly effective, preventive maintenance has its challenges. It should be part of a broader maintenance strategy that includes other methods like predictive maintenance. Some limitations include the possibility of over-maintenance, high initial costs, and the need for skilled personnel. Even with the best plans, preventive maintenance cannot eliminate all risks. Unexpected events such as natural disasters or human errors can still cause failures. Not all equipment is equipped with sensors or monitoring systems. In these cases, manual checks and scheduled maintenance remain necessary. Although less expensive than reactive or predictive approaches, preventive maintenance still requires investment. Small businesses may struggle to fund all required tasks. Some maintenance tasks require equipment to be shut down, which can affect production schedules. Time management becomes crucial, especially in resource-limited environments. Effective preventive maintenance often requires additional staff or extended hours for existing workers. Proper training and resources are essential for success. Performing unnecessary maintenance can waste time, money, and resources. A data-driven approach helps ensure that maintenance efforts are targeted and efficient. There are three main types of preventive maintenance: This type of maintenance follows a fixed schedule, such as monthly or yearly checks. For example, changing an air filter every three months is a common time-based task. However, this method can sometimes lead to over-maintenance if the asset is not used frequently. Instead of relying on time, this method uses actual usage data to determine when maintenance is needed. For instance, car maintenance is often based on mileage or engine hours. This approach prevents unnecessary maintenance and ensures that resources are used where they are most needed. Condition-based maintenance involves monitoring the real-time condition of equipment. If signs of wear or degradation are detected, maintenance is scheduled accordingly. Common indicators include unusual sounds, temperature changes, vibrations, or visible damage. Each type of maintenance includes specific tasks categorized by priority and frequency. These can be time-based, usage-based, or condition-based. Examples include mandatory tasks, non-mandatory tasks, pyramiding tasks, inspection tasks, and task-oriented tasks. A preventive maintenance checklist is a list of tasks that must be completed to ensure proper equipment care. It is usually developed with input from maintenance managers, workers, and regulators. Many companies use digital tools to track and document these checklists effectively. Checklists improve accuracy, streamline processes, and enhance worker safety. They also support consistent maintenance practices across teams and departments. Checklists vary by industry but typically cover areas like safety, equipment condition, and compliance. Examples include building maintenance, IT systems, and vehicle upkeep. Drones are increasingly used in preventive maintenance to perform visual inspections and monitor equipment conditions. They offer a safe, efficient, and cost-effective alternative to traditional methods. For example, the Elios 3 drone is used for inspecting complex infrastructure without requiring shutdowns or scaffolding. This technology enhances safety and reduces downtime while providing detailed reports on asset conditions. With drones, inspectors can access hard-to-reach areas without risking their safety, making preventive maintenance both smarter and more reliable. Ultra High Pressure Cleaning Hose Ultra High Pressure Cleaning Hose is a specialized type of hose used in industrial and commercial applications for high-pressure cleaning and washing. These hoses are designed to withstand extremely high pressure and are typically used in environments where there is a need for powerful and thorough cleaning, such as in industrial settings or in the cleaning of heavy equipment. Surface Cleaning Water Hose,Pressure Washer Hose,Fiber Braided Rubber Hose Luohe Letone Hydraulic Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.litonghose.comPreventive Maintenance: A Comprehensive Guide
What Is Preventive Maintenance?
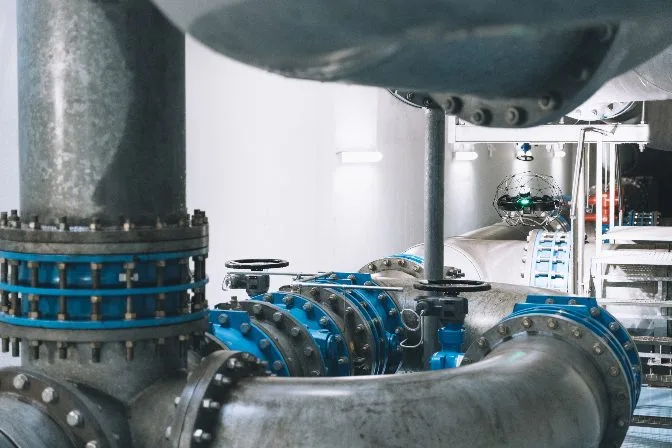 The Elios 3 inspecting a water management system
The Elios 3 inspecting a water management systemWhy Is Preventive Maintenance Important?
Advantages of Preventive Maintenance
Minimizes Downtime
Maximizes Equipment Lifespan
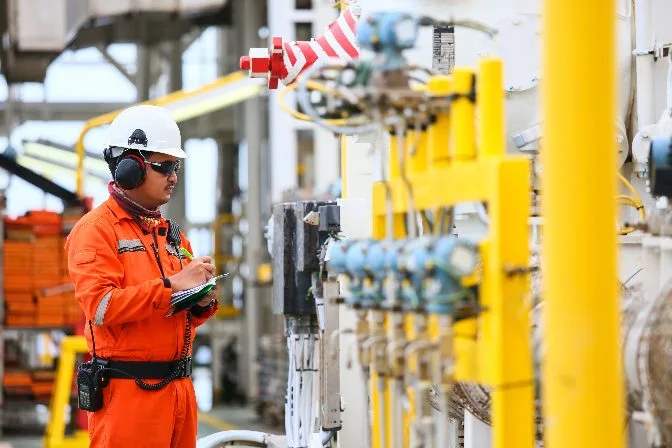

Helps Keep Workers Safe
Helps Ensure Regulatory Compliance
Limitations of Preventive Maintenance
Success Rate
Technological Constraints
Up Front Costs
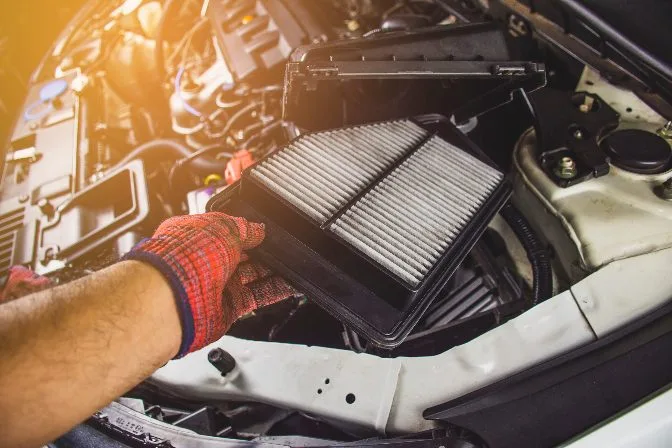 Changing a car filter
Changing a car filterTime Constraints
Worker Limitations
Over Maintenance
What Are the Types of Preventive Maintenance?
Time-Based Maintenance
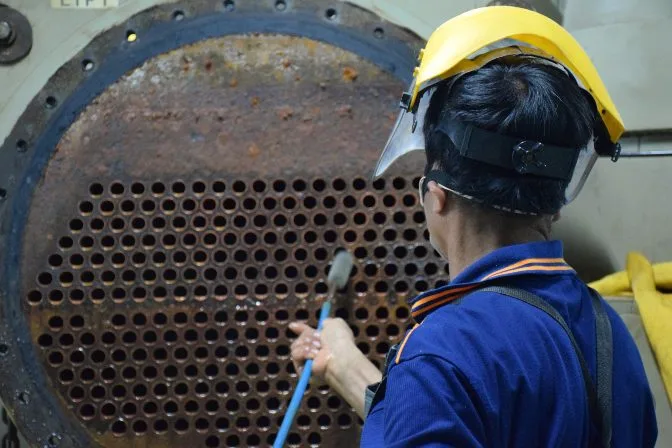 Cleaning a condenser tube from a chiller
Cleaning a condenser tube from a chillerUsage-Based Maintenance
Condition-Based Maintenance
Types of Preventive Maintenance Tasks
What is a Preventive Maintenance Checklist?

Benefits of a Preventive Maintenance Checklist
Preventive Maintenance Checklist Examples
Drones in Preventive Maintenance
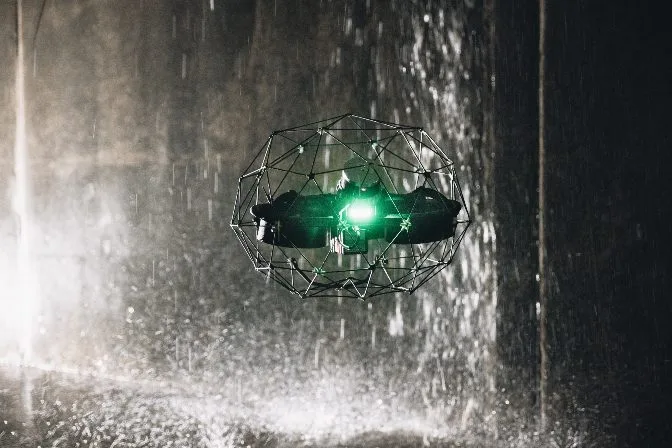 An Elios 3 drone performing a visual inspection
An Elios 3 drone performing a visual inspection
Ultra High Pressure Cleaning Hoses are typically made of materials such as thermoplastic or synthetic rubber, which provide excellent resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and weathering. They are reinforced with high-strength materials such as steel wire or synthetic fibers, which enable them to withstand high-pressure applications without degrading or failing.